
| Home | People | Research | Publications | Demos |
| News | Jobs |
Prospective
Students |
About | Internal |

Visual Understanting of Complex Human Behavior
Automated understanding human behavior in visual signals via computational machinery has been a fundamental topic ever since the inception of machine vision. After decades of research efforts, the recent interests of both the academic and industrial communities have turned to the analysis of complex events in open-source video, where there still remain considerable challenges for current video understanding technology. Besides its scientific value for machine perception, the urgent surge of interests in this topic is triggered by its practical significance in effectively and efficiently processing tremendous amount of video data generated by mobile recording devices ubiquitous worldwide and shared across the Internet 24/7, where it plays a critical role in applications such as media repository management, customized information retrieval & feeds, security & surveillance, among many others.
This work is part of our efforts in video understanding, which aims to enable intelligent anaylsis, encoding and retrieval of informative and semantic content from open-source video data (e.g., those typical sequences on YouTube). Specifically, the goal of the work is to establish a systematic framework consisting of 1) a principled representation platform to capture the critical visual content of complex events at the semantic level; 2) a suite of technical toolkit for efficiently and effectively encoding, learning and reasoning with the representation; 3) a family of classifiers that identifies target action, activity, or event in open-source video based on the representation; and 4) a collection of interfaces that facilitate convinient integration of semantic video understanding for other applicatoins, with several examples implemented for target event recounting, semantic video retrieval via natural language description.
| We propose an adaptive pooling scheme that tailors the pooling operator for each video sequence according to the target event, enabling the content-based video segmentation in a dscriminative fashion. We develop an efficient algorithm to solve the non-linear interger programming for inferece and a convex-concave procedure for learning. |
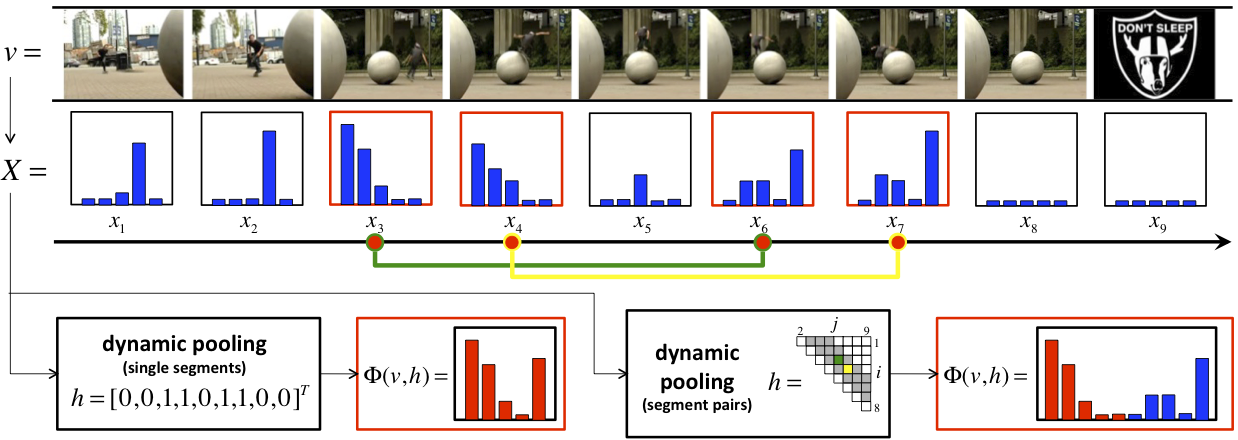
[ project | publications ] |
| In this project, we propose to reprenst a complex video event via a hierarchy of three layers to account for distinct properties at different temporal scales. While the low-level motion signal is encoded by prototype quantization (e.g., BoVW), the critical mid-level activity is modeled by its evolution pattern in the semantic attribute space, which is captured by the binary dynamic system (BDS). The whole complex event is summarized by computing the statistics of the mid-level activities from all snippets. This framework is shown to bridge the gap between low-level visual signal and high-level concept reasoning, and provides a general platform for many applications via video understanding such as event recognition, video summarization, semantic retrieval, and so forth. |
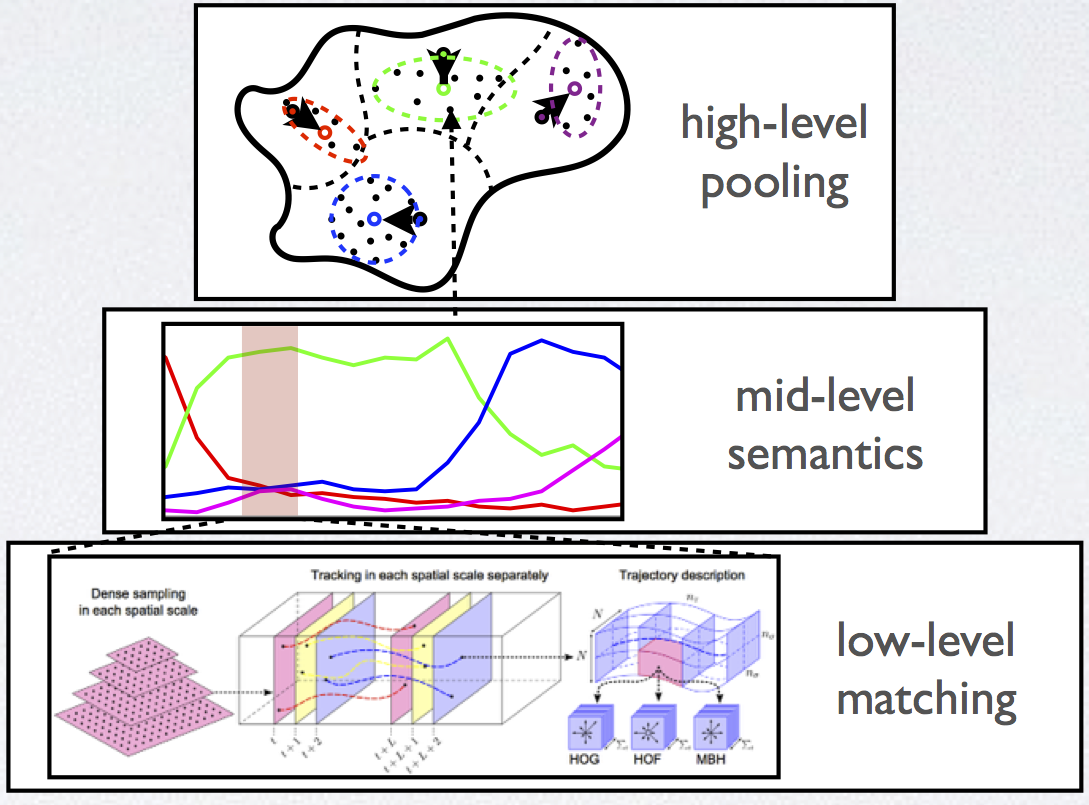
[ project | publications ] |
| This work is an extension to our prvious project of complex event recognition via attribute dynamics. We show that, instead of using manually defined supervised visual attributes, implicit visial stimuli patterns learnt by deep networks can also provide a good basis of semantic responses for mid-level activity modeling. Further more, evolution patterns learnt on both bases are complementary to eath other and combination of both leads to state-of-the-art performance on several action recognition benchmarks. |
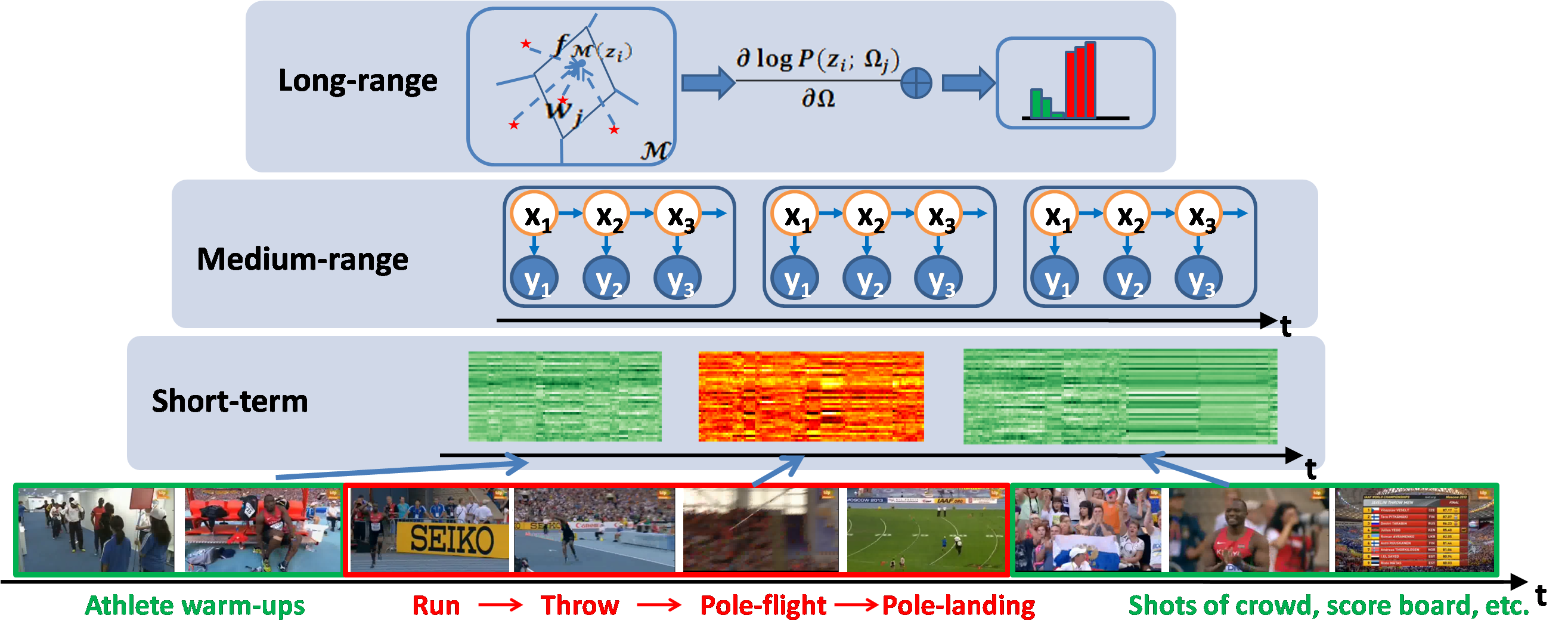
[ project | publications ] |
Dynamic Pooling for Complex Event Recognition
Wei-Xin LI,
Qian Yu,
Ajay Divakaran
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
Proc. of
IEEE International Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV)
Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, 2013
[
pdf |
DOI |
BibTeX
]
Multiple Instance Learning for Soft Bags via Top Instances
Wei-Xin LI,
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Boston, Massachusetts, United States, 2015
[
pdf |
DOI |
BibTeX
]
Visual Understanding of Complex Human Behavior via Attribute Dynamics
Wei-Xin LI
Ph.D. Dissertation, UC San Diego, 2016
[
pdf |
BibTeX
]
Complex Activity Recognition via Attribute Dynamics
Wei-Xin LI
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)
to appear in the printed version,
available
online on June 21, 2016
[
preprint (pdf) |
DOI |
BibTeX
]
Recognizing Activities via Bag of Words for Attribute Dynamics
Wei-Xin LI,
Qian Yu,
Harpreet Sawhney
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
Proc. of
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Portland, Oregon, United States, 2013
[
pdf |
DOI |
BibTeX ]
Recognizing Activities by Attribute Dynamics
Wei-Xin LI
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS)
Lake Tahoe, Nevada, United States, 2012
[
pdf |
BibTeX ]
VLAD3: Encoding Dynamics of Deep Features for Action Recognition
Yingwei Li,
Wei-Xin LI,
Vijay Mahadevan
and
Nuno Vasconcelos
Proc. of
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Las Vegas, Nevada, United States, 2016
[
pdf |
DOI |
BibTeX
]
![]()
©
SVCL